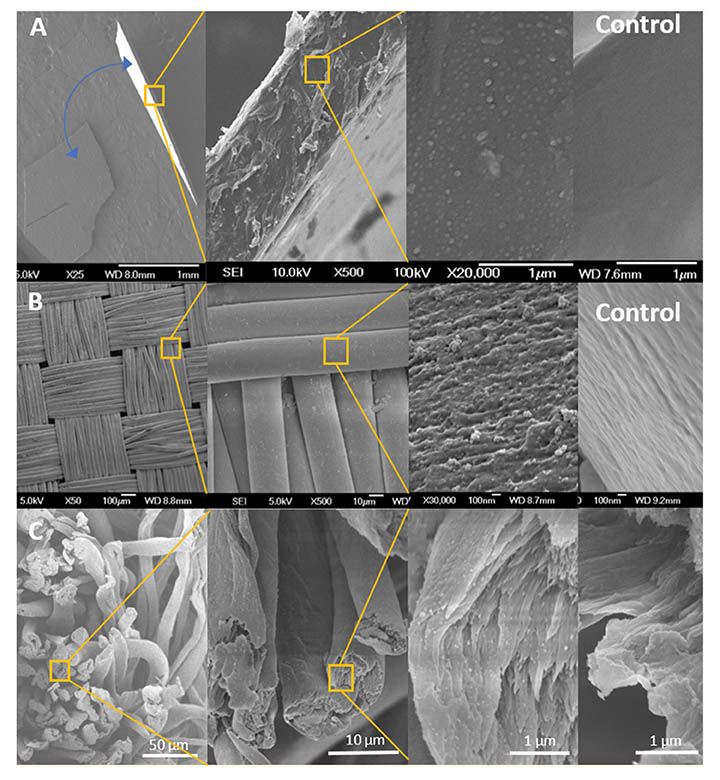
Figure 2. SEM images of plastic nanocomposites produced with “in situ growth” process. (A) Zinc-polyurethane nanocomposite film. The blue arrows show two pieces of the nanocomposite thin film. Image amplification at the film cross-section shows the presence of zinc nanoparticles inside the film. (B) Zinc-nylon nanocomposite showing zinc nanoparticles embedded with the nylon fibers. (C) Silver-polyester/cotton nanocomposite.
Highly efficient and durable antimicrobial nanocomposite textile